Difference between revisions of "Walkthrough on GUI based tilt series alignment"
(→Data) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
The basic function for invoking the GUI is <tt>dtsa</tt> (short form of <tt>dynamo_tilt_series_alignment</tt>; | The basic function for invoking the GUI is <tt>dtsa</tt> (short form of <tt>dynamo_tilt_series_alignment</tt>; | ||
| − | <tt>u = dtsa( | + | <tt>u = dtsa();</tt> |
| + | |||
| + | Here, <tt>u</tt> is an object that will reside in memory during the session and allows to interoperate with the workflow through the command line. It is not necessary when proceeding through the GUI. | ||
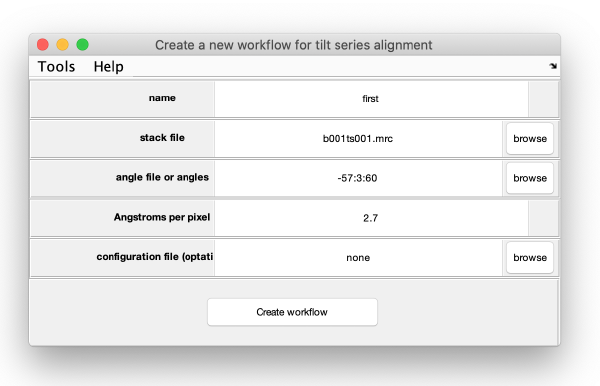
[[ File:alignGUI_creatingAWorkflow.png |thumb|center| 600px|creating a workflow]] | [[ File:alignGUI_creatingAWorkflow.png |thumb|center| 600px|creating a workflow]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
[[ File:alignGUI_inputWorkflowParameters.png |thumb|center| 600px|input workflow parameters]] | [[ File:alignGUI_inputWorkflowParameters.png |thumb|center| 600px|input workflow parameters]] | ||
| + | |||
= GUI description = | = GUI description = | ||
Revision as of 09:58, 27 August 2019
Dynamo includes a package for automated aligned and reconstruction of tilt series. This walkthrough guides you through the steps on how to use it with a GUI. A different page in this wiki
Contents
Data
We have prepared a version of a tilt series from the EMPIAR entry [XXXX]
wget https://wiki.dynamo.biozentrum.unibas.ch/html/w/doc/data/hiv/align/b001ts001.mrc
In this binned version, the pixel size is 2'7 Angstrom (original was 1.35, this is bin level 1 in Dynamo)
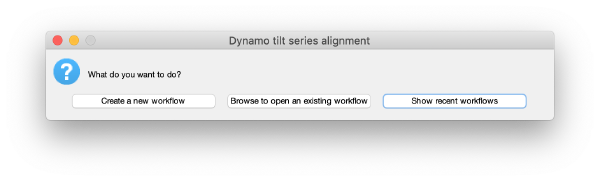
Creating an alignment workflow
The basic function for invoking the GUI is dtsa (short form of dynamo_tilt_series_alignment;
u = dtsa();
Here, u is an object that will reside in memory during the session and allows to interoperate with the workflow through the command line. It is not necessary when proceeding through the GUI.
The data for the workflow (tilt series, angles) could have been introduced directly when creating the workflow, we however will introduce each item explicitly in this walkthrough.
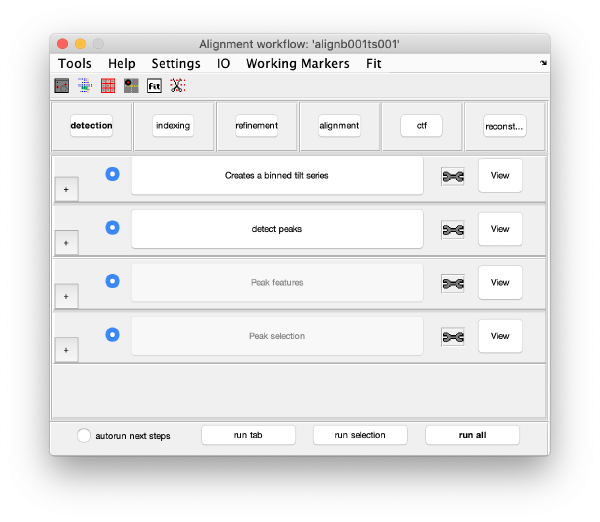
GUI description
The GUI guides of the process of creating and editing a set of "working markers" (in the areas of detection, reindexing and refinement), and then using them to create aligned stacks (alignment tab), analyse and correct their CTF (through wrappers to ctfffind4 and imod) and then create reconstructions.
Settings
Acqusition settings
Here you enter pixel size (2.7 Angstroms), Cs (2.2), nominal defocus (-4.0 microns, used if the CTF area is connected).
Controls
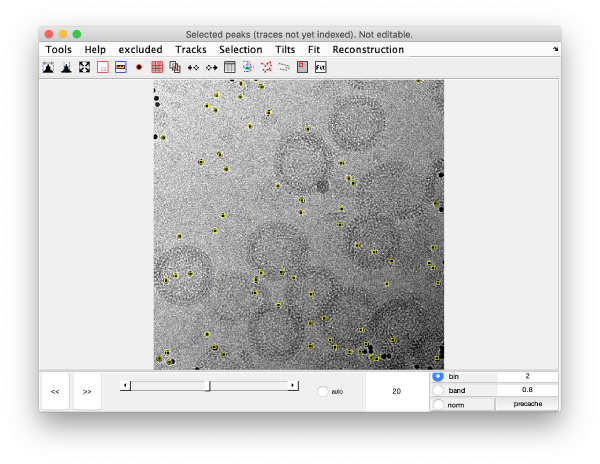
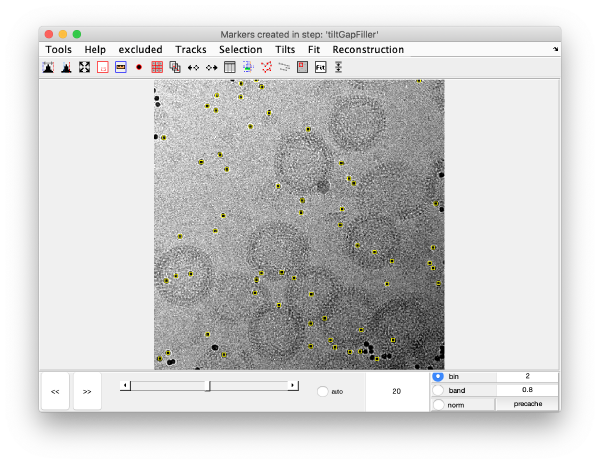
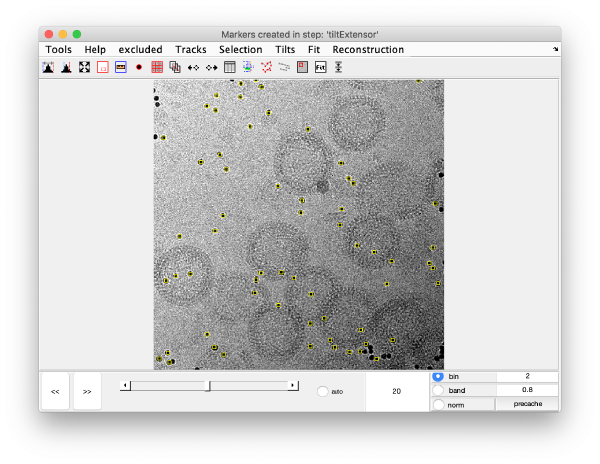
markers GUI
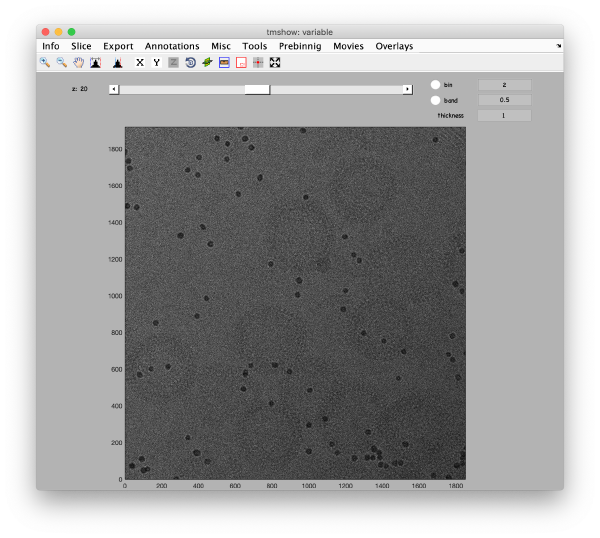
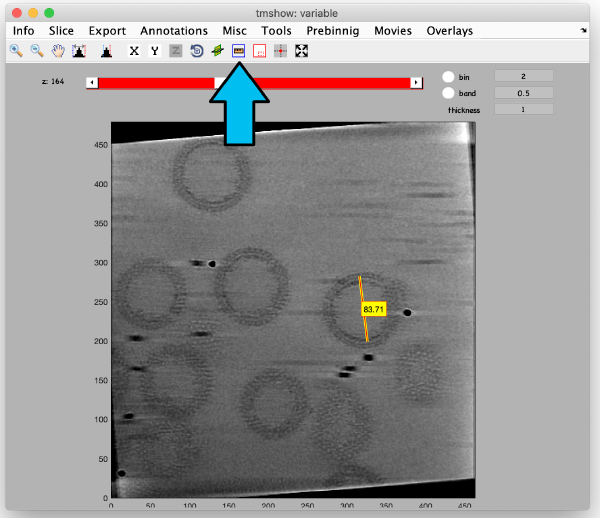
The icon of the markers GUI allows you to check the position of the working markers in the micrograph. If you want to make editions of the GUI permanent, you need to save the current markers.
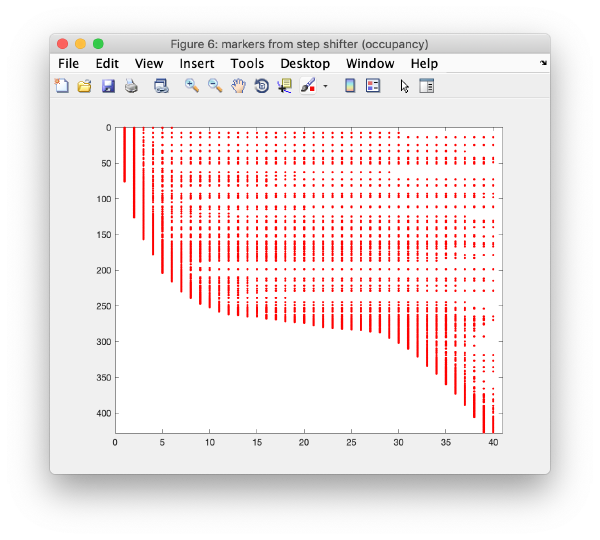
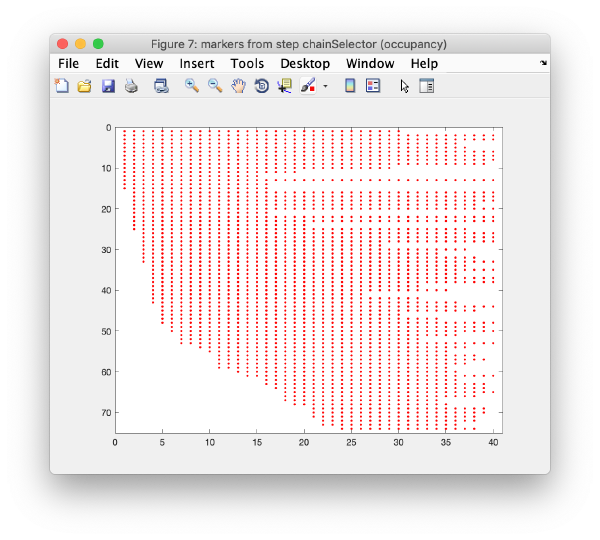
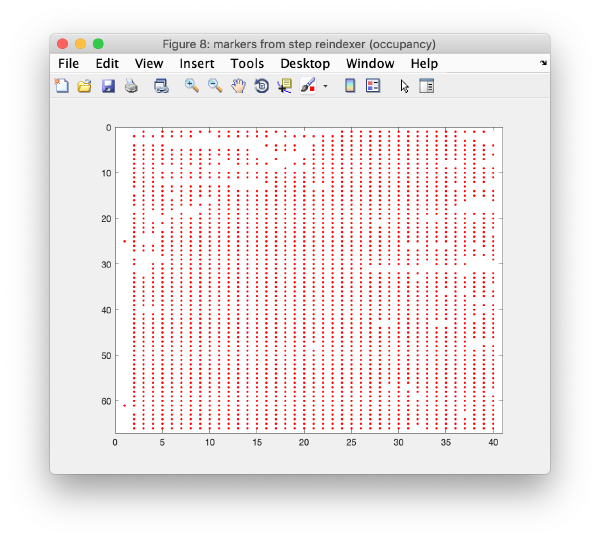
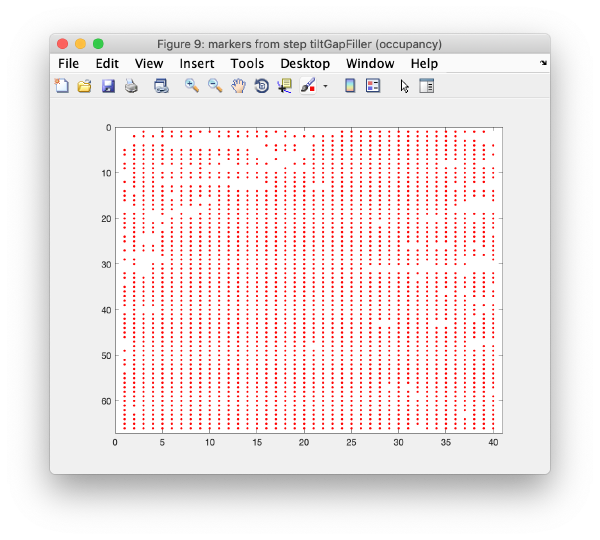
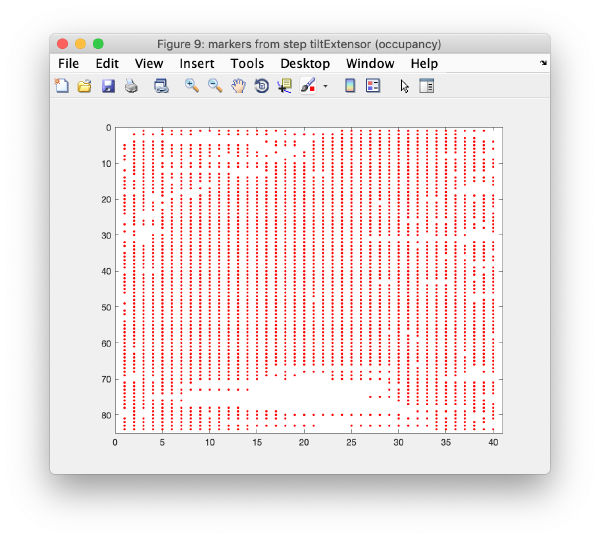
Occupancy plot
Shows a scheme of which markers are present in which tilt numbers.
Gold bead gallery
Crops the gold beads currently contained in the working markers and shows them as a gallery.
Execution Areas
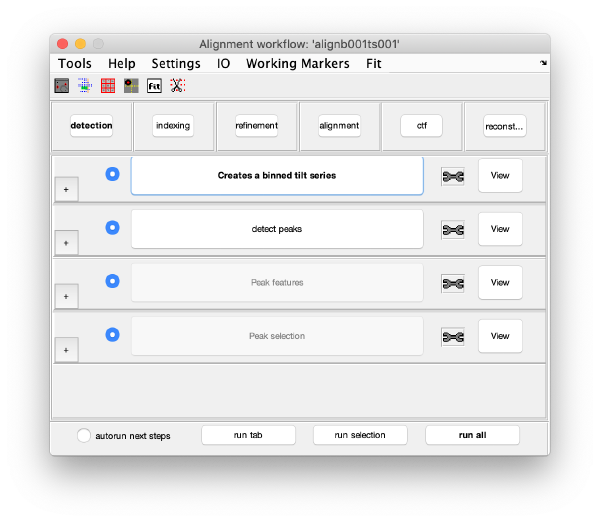
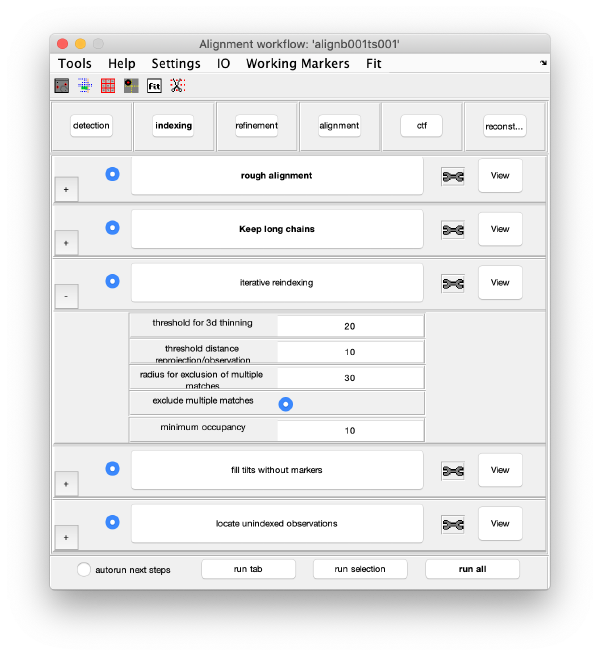
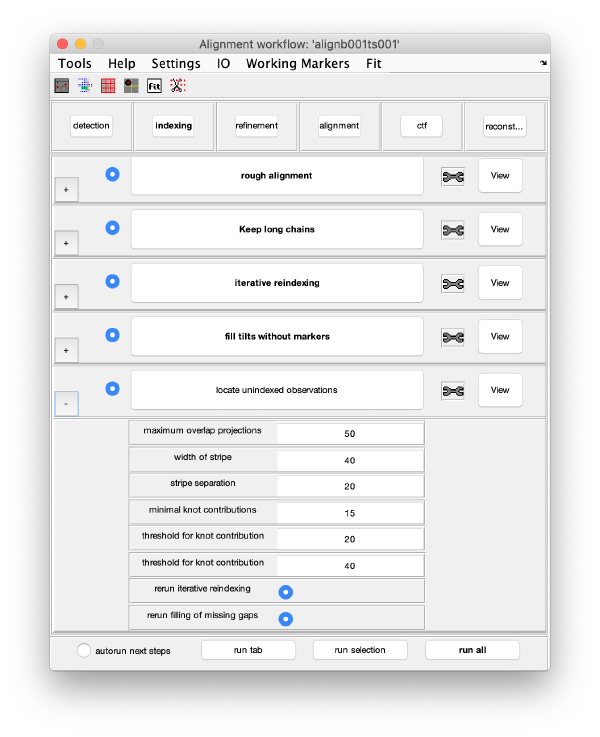
The GUI is divided in five areas, which are sets of steps that can be executed sequentially. Sequential execution is the natural way of proceeding; but steps can be visited in any order, i.e., a step can be reexecuted in a later moment after updating its information.
Steps
Steps needs to be open (letters in grey) in order to be executed. They become open when the input they require gets computed and stored during execution of the workflow. When a step is under execution, its pushbutton becomes green.
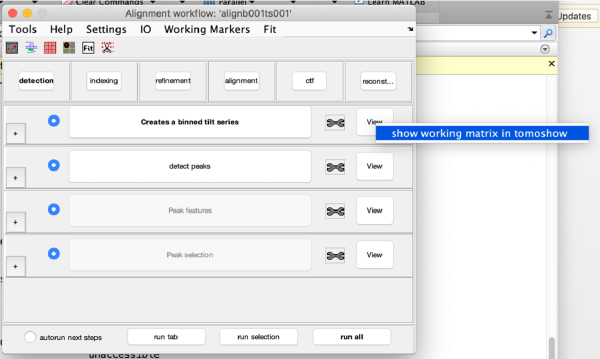
Step Toolbox
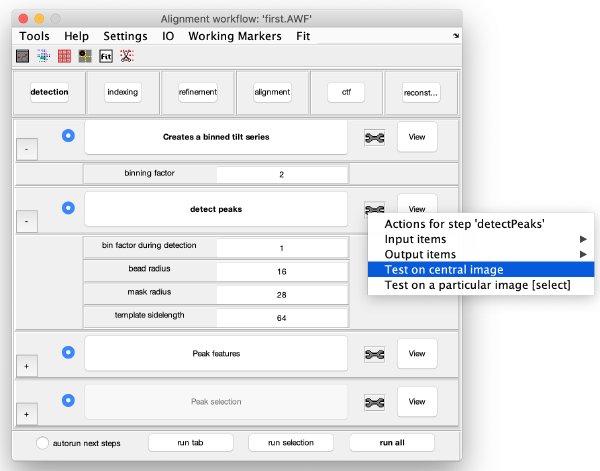
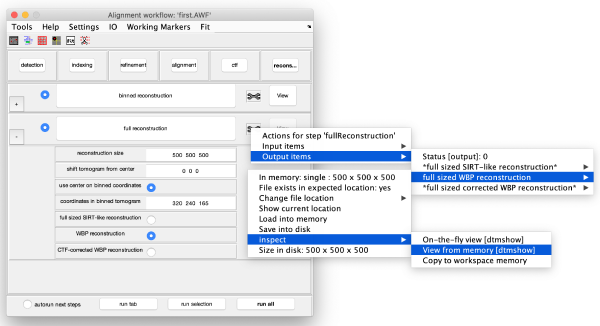
The tool icon can be secondary clicked and will provide a popup menu with specific tools for each steps and some common one. The common ones are handles to inspect and list the items that are needed (input items) or generated (output items) by the step. The View provides tools specific for visualisation of results of the step.
Entering the data
The minimal data to initiate. w work
- tilt series matrix.
- tilt angles.
- discarded tilt angles
Discarded tilt angles
Tilt angles to be discarded can be selected directly with the dmarkers GUI using the x and shift + x buttons.
The areas in the alignment task
Detection
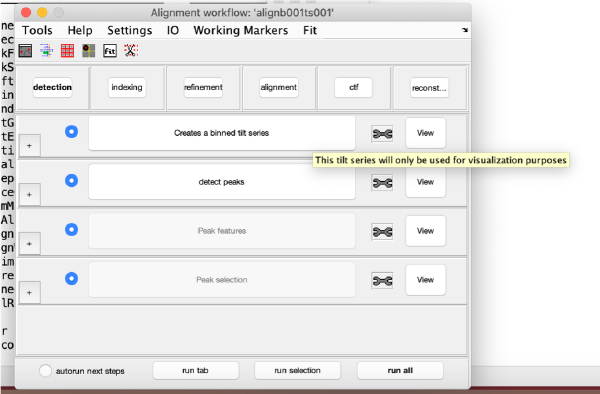
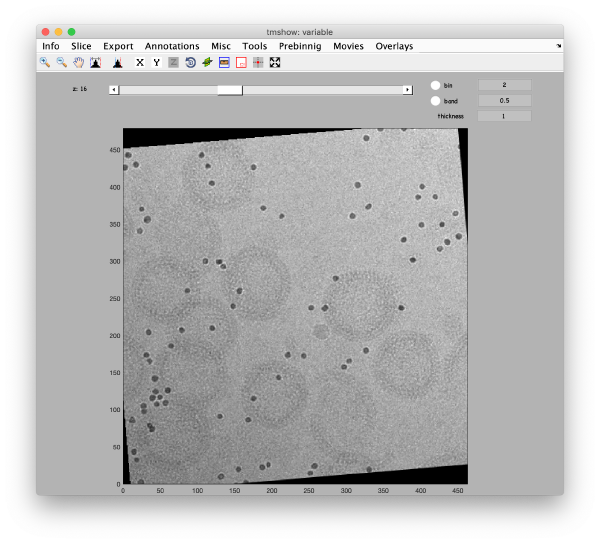
Visualization matrix
This step just creates a binned version of the tilt series stack to accelerate visualizations that will be invoked in a later point.
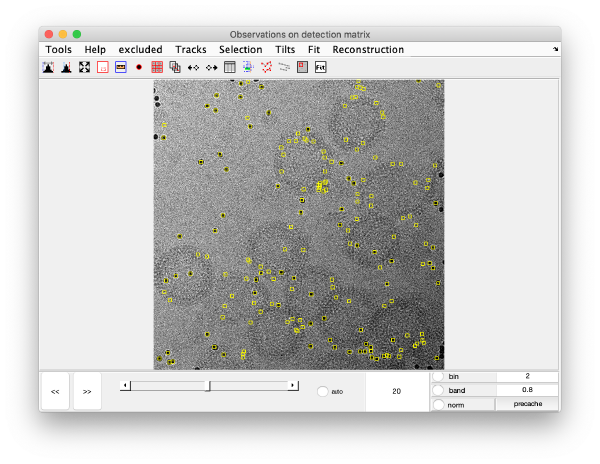
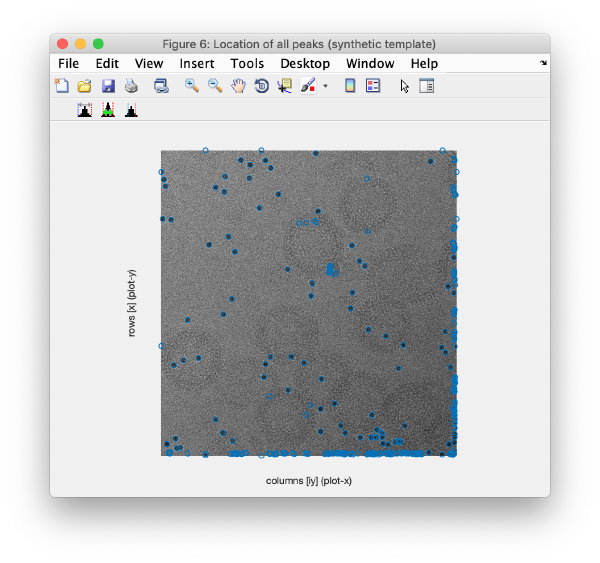
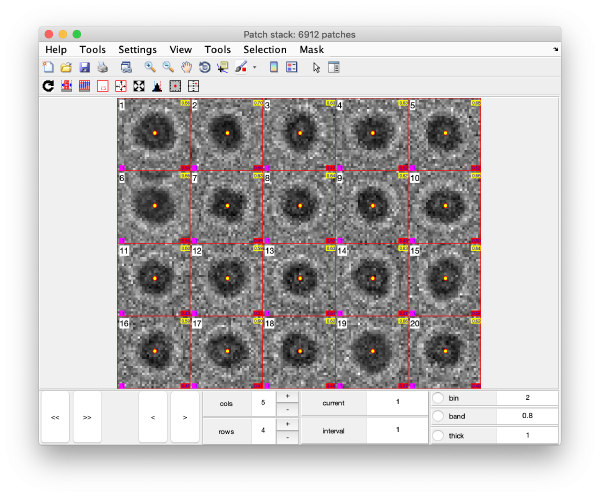
Detection of gold beads
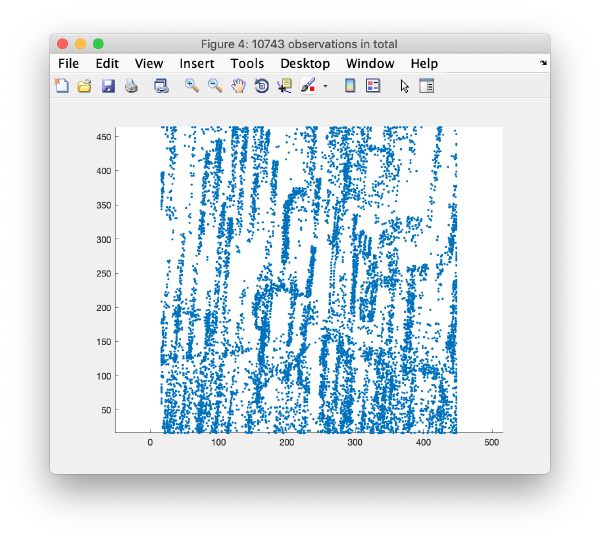
Computation of observation features s
Selection of best gold beads
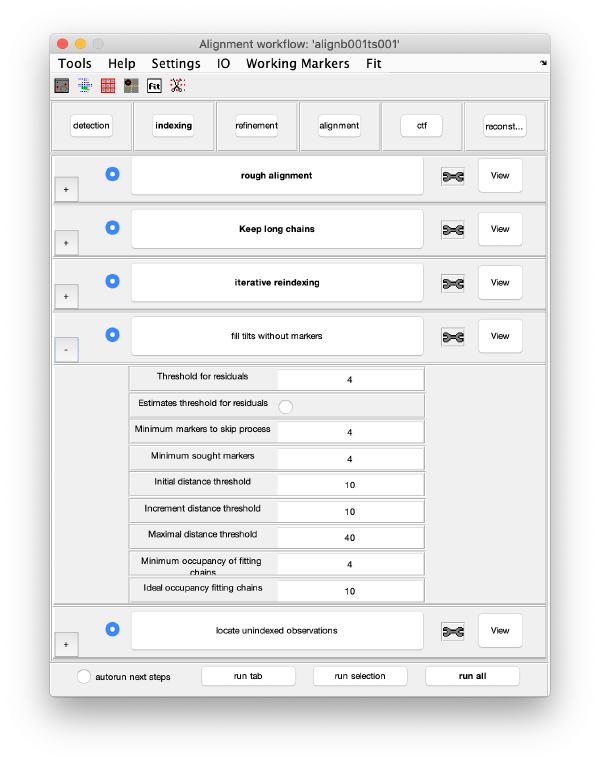
Indexing
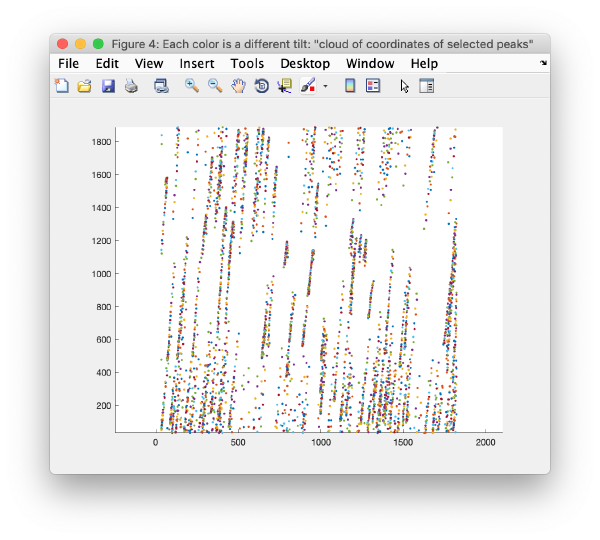
Rough Alignment
Selection of stable trails
Iterative reindexing
Tilt gap filling
Trail extension
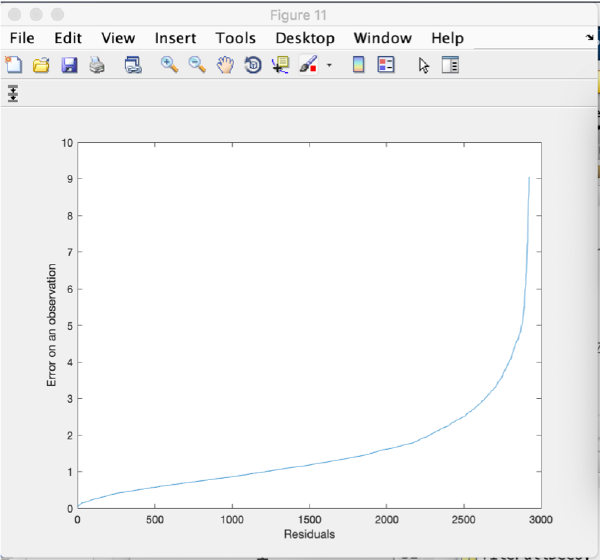
Refinement
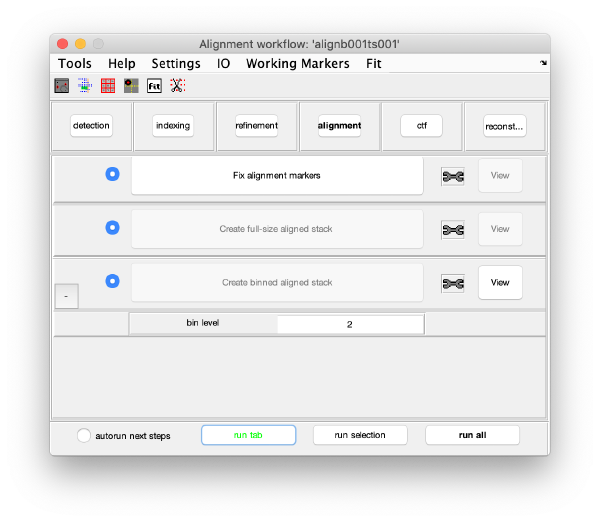
Alignment
Fix the markers
Align the tilt series
CTF
In this GUI CTF estimation and correction are delegated to CTFFIND4 and Imod's ctfphaseflip programs respectively. This part will not be used in the workshop.'
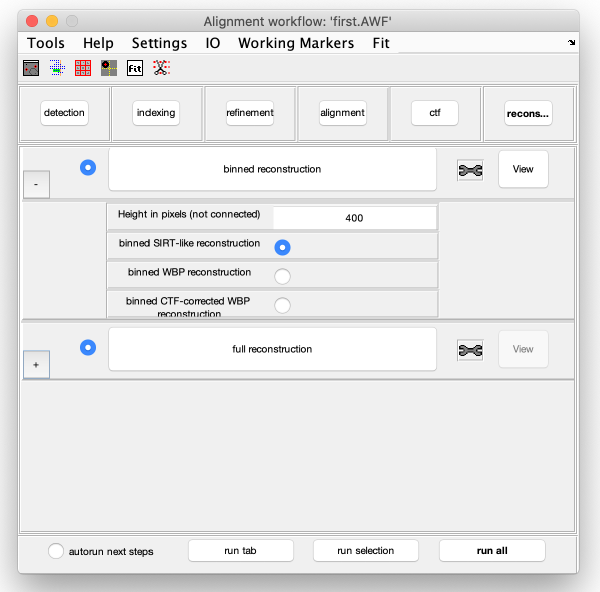
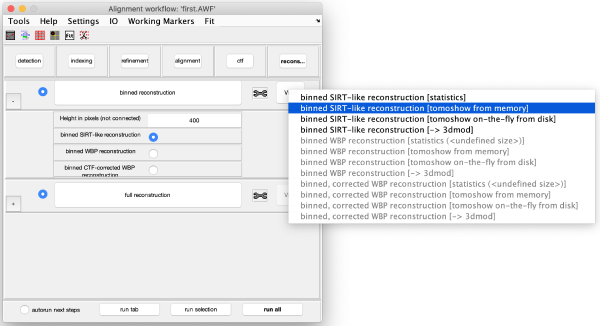
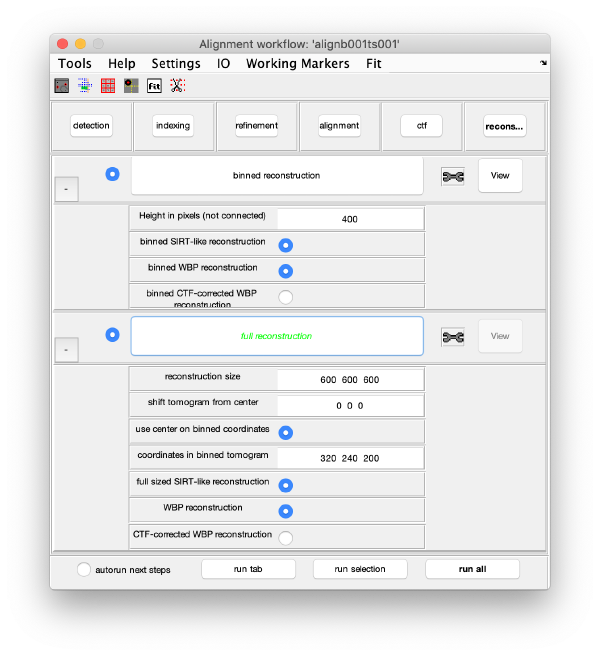
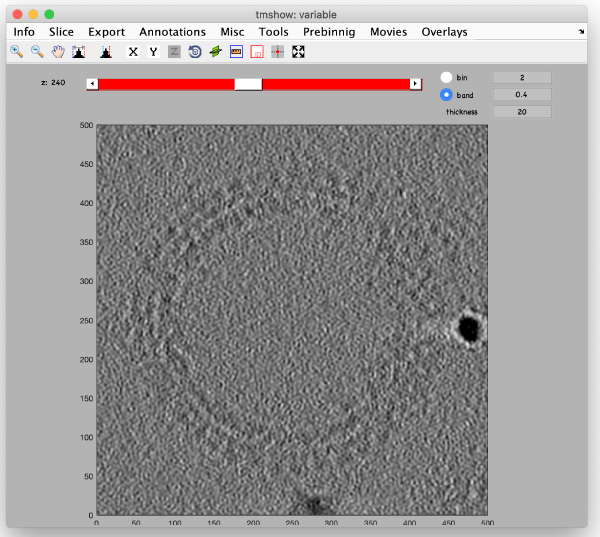
Reconstruction
Binned reconstruction
Full sized reconstruction
]